Chưa được phân loại
Exercises about Claisen condensation
The Claisen Condensation
The nucleophilic carbon of the enolate ion adds to the electrophilic carbon of a molecule of ethyl acetate that has not been deprotonated. A carbon-carbon bond is formed. The reaction produces yet another tetrahedral intemediate as shown in Equation 1.
Since the newly formed tetrahedral center has an electronegative atom attached to it, reformation of the carbonyl group, as shown in Equation 2, is a reasonable process.
Exercise 1
Draw the structure of the major product you would expect to be formed in each of the following situations:
Exercise 3:
An intramolecular version of the Claisen condensation is known as the Dieckmann condensation. Equation 3 shows how this reaction was put to good use as part of the total synthesis of the prostaglandin PGA2.
Equation 4 offers another example of the Dieckmann condensation that was involved in the synthesis of tropinone, a degradation product that was produced during the determination of the structure of the physiologically active alkaloid atropine.
Example 4 :Dieckmann Condensation
Example 5 :Crossed Claisen Condensation
Example 6:
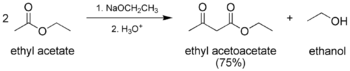
The classic Claisen condensation, a self-condensation between two molecules of a compound containing an enolizable ester.
Example 7:
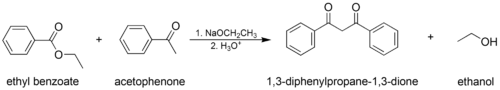
The mixed (or “crossed”) Claisen condensation, where one enolizable ester or ketone and one nonenolizable ester are used.
Example 8:
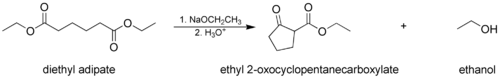
The Dieckmann condensation, where a molecule with two ester groups reacts intramolecularly, forming a cyclic β-keto ester. In this case, the ring formed must not be strained, usually a 5- or 6-membered chain or ring.
Example 9:
The Stobbe condensation [5] is a modification specific for the diethyl ester of succinic acid requiring less strong bases.[6]An example is its reaction with benzophenone:[7]
A reaction mechanism that explains the formation of both an ester group and a carboxylic acid group is centered around alactone intermediate (5):